Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Evolving Threats: The cybersecurity landscape is rapidly changing, with more sophisticated and automated attacks emerging.
- Critical Vulnerabilities: IoT devices and supply chain systems are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals.
- Proactive Prevention: Implementing robust cybersecurity frameworks and employee training is essential.
- Future Outlook: Organizations must prepare for challenges like quantum computing threats and new regulations.
Table of Contents
The Evolving Cybersecurity Landscape
The cybersecurity landscape in 2025 is marked by both opportunity and risk. The advent of artificial intelligence and automation provides tools for both defense and attack. With technology advancing rapidly, the complexity of cybersecurity threats has increased exponentially. Key trends in this evolving environment feature:
- Widespread adoption of cloud technologies
- Proliferation of IoT devices
- Advanced AI-powered attack methods
- Increased geopolitical cyber warfare
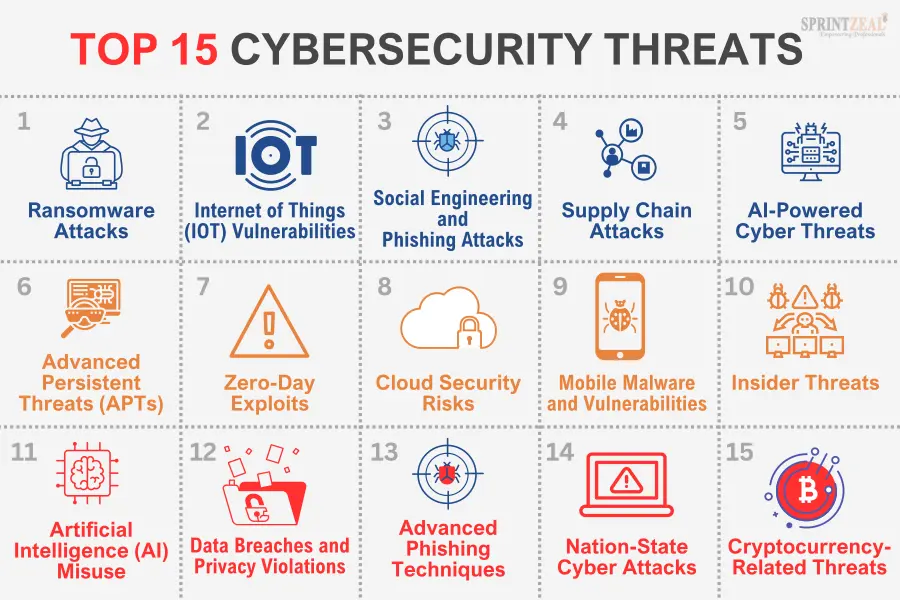
Latest Cyber Threats in 2025
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs have evolved into highly sophisticated, long-term attack campaigns. They frequently target hefty organizations like government institutions and critical infrastructure. Stealth attacks can go undetected for months, exfiltrating sensitive data in the process. [Source: Google Cloud]
Ransomware Evolution
Ransomware tactics now involve double extortion, supply chain targeting, and automated propagation methods. These advanced threats pose high risks to sensitive data security. [Source: SentinelOne]
AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
Artificial intelligence introduces threats such as self-modifying malware, adaptive attack patterns, and intelligent evasion techniques, enhancing the capabilities of cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities more effectively. [Source: IBM Think]
IoT Vulnerabilities
The widespread adoption of IoT devices brings security challenges like weak authentication mechanisms and insufficient encryption, drawing the eye of cyber adversaries. [Source: ConnectWise]
Supply Chain Attacks
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting third-party vendors to exploit vulnerabilities within software dependencies and cloud services, amplifying the potential damage across multiple organizations. [Source: Google Cloud]
Zero-Day Exploits
With an increased rate of discovery, zero-day exploits represent a major threat due to their ability to bypass traditional defenses, making them a lucrative target for hackers. [Source: ConnectWise]
Impact Assessment
Financial Impact
- Direct monetary losses
- Operational disruption costs
- Legal penalties and fines
Reputational Damage
- Loss of customer trust
- Brand deterioration
Operational Disruption
- System downtime
- Data loss
Cyber Risk Prevention Strategies
Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Frameworks
Organizations should integrate comprehensive security frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001 for ongoing protection and compliance. [Source: Google Cloud]
Employee Training and Awareness
An informed workforce is crucial to maintaining security hygiene and swiftly identifying threats. [Source: SentinelOne]
Regular Security Assessments
Regular vulnerability scanning and risk assessments are vital for maintaining an up-to-date defensive posture. [Source: Google Cloud]
In addition to technical strategies, continuous learning can boost your team’s cybersecurity skills. Explore [comprehensive web tutorials](https://trendflo.net/your-ultimate-guide-to-comprehensive-web-tutorials/) for enhanced measures.
Best Practices for 2025
Maintain a strong cybersecurity posture by:
- Implementing zero-trust architecture
- Utilizing AI-powered security tools
- Conducting continuous monitoring
- Fostering a culture of security awareness
Future Outlook
Beyond 2025, companies should brace for future challenges, including quantum computing threats, advanced AI-driven attacks, and expanded attack surfaces.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity threats of 2025 demand a vigilant and adaptable approach. Combining technical solutions with skilled personnel and constant vigilance is key to a resilient cybersecurity strategy.
For further guidance, explore resources like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or the ISO/IEC 27001 Documentation. Also, expand your knowledge with our comprehensive web tutorials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)?
APTs refer to stealthy, prolonged cyber-attacks targeting significant entities such as governments and infrastructure, often executed over extended periods.
How can organizations counteract AI-powered cyber threats?
Implementing AI-driven defense mechanisms and continuous monitoring are crucial in combating AI-powered cyber threats effectively.
Why are IoT devices particularly vulnerable?
IoT devices often possess weak security settings and limited update capabilities, making them susceptible to cyber attacks.
What is a zero-trust architecture?
Zero-trust architecture is a security model that requires authentication and verification at every access point within an organization’s network.
How should companies prepare for quantum computing threats?
Staying abreast of emerging technology and investing in quantum-resistant encryption and key management systems can help mitigate potential quantum computing threats.









